Functional Neurological Disorder Guide
By Jenny Walker.
Introduction
When a person receives a diagnosis of Functional Neurological Disorder, there is a lot of information to take in and it can feel overwhelming. FND occupies a grey area between psychiatry and neurology. It may not feel easy to know where to turn for information. We hope this report provides clear information to help you navigate the complexities of living with FND.
Functional Neurological Disorder
Functional Neurological Disorder (FND) is a problem concerning how the brain and body send and receive signals. There is no structural damage to the brain, but rather an abnormality in how it is functioning. Sigmund Freud named it Conversion Disorder as he believed it was a psychological disorder that converted into a neurological one.
There are many types of FND, but they can be primarily categorised into psychogenic nonepileptic seizures (PNES) and functional movement disorder. Functional movement disorder FND affects the motor system (movement) and is the focus of this post.
Symptoms
A person with FND may find their symptoms fluctuate. Symptoms can be physical, sensory, or cognitive. This means it can affect muscle movements, memory, concentration, cognition, and the processing of sensations.
How does FND present?
- Leg and arm weakness or paralysis
- Tremor
- Sudden, brief, involuntary twitching or jerking (myoclonus)
- Involuntary muscle contractions causing slow repetitive movements (dystonia)
- Problems with walking motion, posture, or balance
- Spasms and contractures
- Muscle stiffness
- Tics
- Speech difficulties
- Visual or audio difficulties
- Pain (including migraines)
- Extreme slowness and fatigue
- Numbness or inability to sense touch
Symptoms appear suddenly and can rapidly progress, however, they may also be decreased, for example when you are distracted.
Causes
The exact cause of FND is unknown, however, there are common causes including illness, physical injury, anxiety, trauma, and stress.
Anyone can develop FND although it is more common in women. It is uncommon in children under 10 years old.
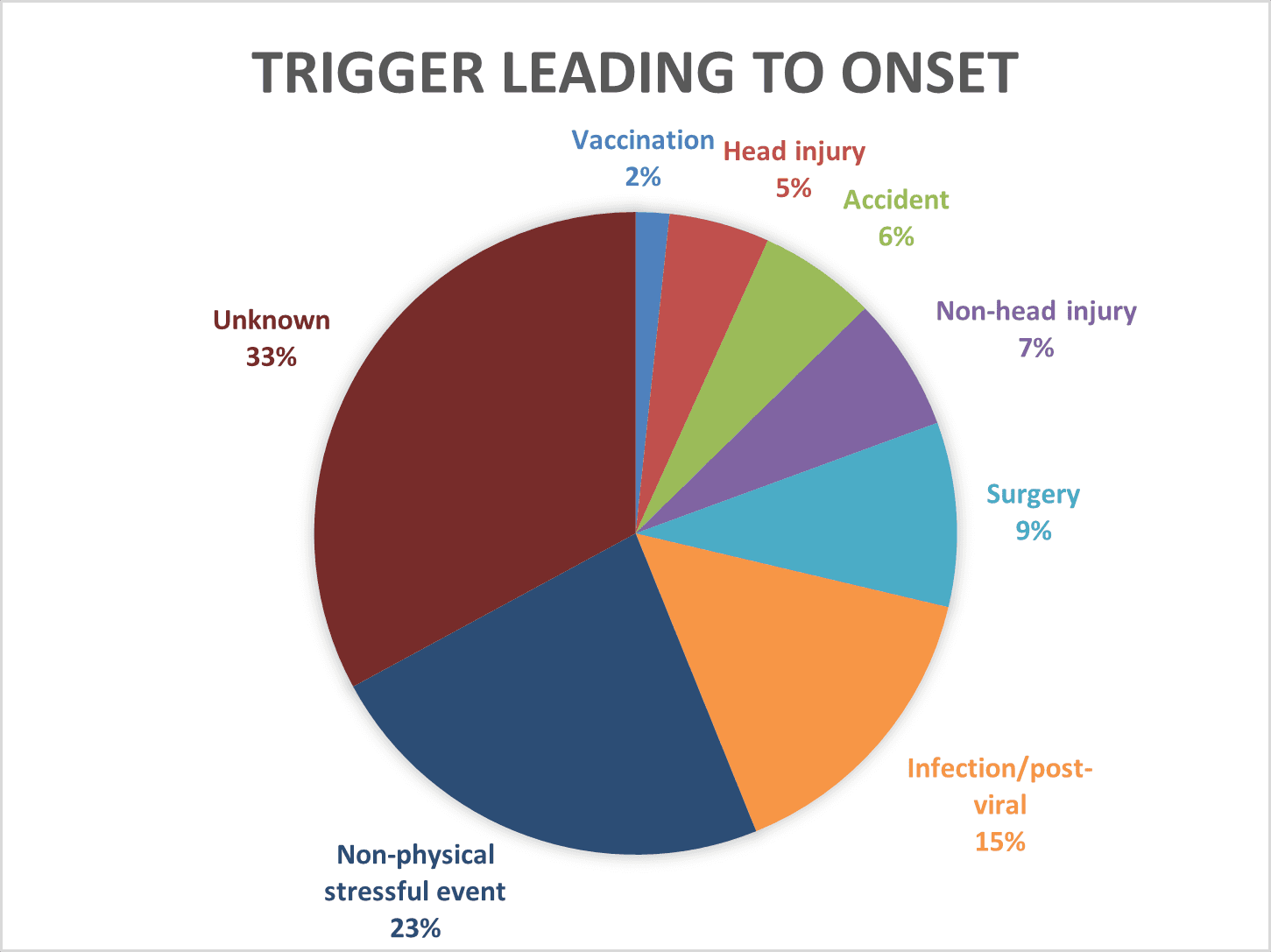
FND Hope conducted a study asking patients what triggered their onset. Below is an adaptation of the findings.
Diagnosis
A health and medical assessment should be undertaken, to rule out other neurological conditions. This is because functional disorders can co-exist with other conditions. A neurologist and a psychiatrist will look at patterns of movement and symptoms to help diagnose the disorder.
Treatment
People with FND have the potential to make a full recovery, however, some people may battle with FND in the long term.
Approaches to treatment include:
- Psychological input and cognitive behaviour therapy
- MDT approach
- Identifying and managing triggers
- Family help to understand FND Medications are available to treat underlying causes such as anxiety, as well as symptoms such as pain
- Relaxation and mindfulness
- Physical therapy for muscle weakness and impaired movement
- Occupational therapy to improve how you function and perform everyday tasks
- Speech therapy, if ability to swallow is affected
- Advice on distraction techniques
Treatment is most successful when the person feels ready to start treatment. There may be challenges to overcome in order to meet this.
What will happen in the clinic?
You will be assigned an appointment with one of the named physiotherapists at Thorpes Neuro Rehab. They will complete an initial assessment and discuss their findings with you. Together, you will then develop goals to create a treatment plan specific to you. This is a private and confidential time for you to discuss your diagnosis with a health professional.
Warm Regards,
Jenny Walker
Specialist Neurological Physiotherapist
About the author
For over 21 years, 1000's of people have consulted Jenny and her team of Neurological Physiotherapists looking for answers about how to stay more mobile, active, and maintain independence whilst living with Neurological conditions.
For more information:
- Institute's Brain Resources and Information Network (BRAIN) by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. BRAIN, P.O. Box 5801, Bethesda, MD 20824, 800-352-9424
- FND Hope International - https://fndhope.org/contact/
- https://neurosymptoms.org
- Functional Neurological Disorders Society (for physicians and investigators)
Sources
FND Hope, 2021, What is FND, available at https://fndhope.org/fnd-guide/ [Accessed 30/05/2022]
Jungilligens, J., et al., 2022, A new science of emotion: implications for functional neurological disorder, Brain
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, 2022, Functional Neurologic Disorder, available at https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/patient-caregiver-education/fact-sheets/functional-neurologic-disorder [Accessed 07/06/2022]
Stone, J., 2015, Functional neurological disorders: the neurological assessment as treatment, Practical Neurology
Advice disclaimer
We make every effort to ensure that we accurately represent the condition, advice and prognosis displayed throughout this Guide.
However, examples of conditions and their prognosis are based on typical representations of those conditions that we commonly see in our physiotherapy clinic. The information given is not intended as a representation of every individual’s potential condition. As with any condition, each person’s symptoms can vary widely and each person’s progress can also vary depending upon background, genetics, previous medical history, application of exercises, posture, motivation to follow physio advice and various other physical factors.
It is impossible to give a 100% complete accurate diagnosis and prognosis without a thorough physical examination and likewise, the advice given for the management of a condition cannot be deemed fully accurate in the absence of this examination from one of the Chartered Physiotherapists at Thorpes Neuro Rehab.
We are able to offer you this service at a standard charge. Significant injury risk is possible if you do not follow due diligence and seek suitable professional advice about your condition. No guarantees of specific results are expressly made or implied in this report.
Get In Touch
Appointments available Monday to Friday, 8am to 6pm by prior arrangement only.
Please contact us now for further information.
- 0118 391 5055
- office@thorpesneurorehab.com
- Appointments: Mon-Fri 8am-6pm
- Unit 5, Church Farm Business Centre Church Road,
Hook, Hampshire,
RG27 0PX - Our Facebook PageOur Instagram ProfileOur Linkedin Profile